"Buy genuine cefdinir line, antibiotic 8 weeks pregnant".
By: F. Hamil, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Duke University School of Medicine
Fear and a lack of confidence among teachers regarding the education of students with disabilities can be overcome: In Zambia teachers in primary and basic schools had expressed interest in including children with disabilities infection en la garganta purchase cefdinir with a mastercard, but believed that this was reserved for specialists antibiotic nausea cheap cefdinir 300mg free shipping. They were encouraged to discuss their negative beliefs and to write about them reflectively (120) infection pathophysiology purchase cefdinir american express. In Mongolia a training programme on inclusive education was run for teachers and parents with the support of specialist teachers antibiotic 3 day dose cefdinir 300 mg line. The 1600 teachers trained had highly positive attitudes towards the inclusion of children with disabilities and towards working with the parents: the enrolment of children with disabilities in preschool facilities and primary schools increased from 22% to 44% (121). The role of communities, families, disabled people, and children with disabilities Approaches involving the whole community reflect the fact that the child is an integral member of the community and make it more likely that sustainable inclusive education for the child can be attained (see Box 7. These activities are part of the Australian Sports Outreach Program, an Australian government initiative that seeks to help individuals and organizations deliver high-quality, inclusive sport-based programmes that contribute to social development. Sport can improve the inclusion and well-being of people with a disability: by changing what communities think and feel about people with a disability and in that way reducing stigma and discrimination; by changing what people with a disability think and feel about themselves and in that way empowering them to recognize their own potential; by reducing their isolation and helping them integrate more fully into community life; by providing opportunities which assists young people to develop healthy body systems (musculoskeletal, cardiovascular) and improve coordination. In this region a project called Alternative Basic Education for Karamoja has been set up. It encourages the participation of children with disabilities and school instruction in the local language. The Oriang project in western Kenya has introduced inclusive education in five primary schools. Technical and financial assistance is provided by Leonard Cheshire Disability (60). The support includes training new teachers and working with students, parents, teachers, and the wider community to change attitudes and build the right structures for delivering inclusive education. The project benefits 2568 children, of whom 282 have a mild to severe disability (127). The family is the first source of education for a child, and most learning occurs at home. Parents are frequently active in creating educational opportunities for their children, and they need to be brought on board 224 Chapter 7 Education to facilitate the process of inclusion. Inclusion Panama pressured the Panamanian government to change the law requiring children with disabilities to be educated in a separate system. In 2003, as a result of its campaign, the government introduced a policy to make all schools inclusive. The Southern Africa Federation of the Disabled, for instance, has set up a range of programmes involving people with disabilities, including its children and youth programme, running for the past 15 years. The programme focuses on all aspects of discrimination and abuse of children with disabilities and their exclusion from education and other social activities. However such organizations frequently lack the resources and capacity to develop their role in education. Children with disabilities the voices of children with disabilities themselves must be heard, though they frequently are not. In recent years children have been more involved in studies of their experiences of education. The results of such childinformed research are of great benefit for educational planners and policy-makers and can be a source of evidence as educational systems become more inclusive. Audiovisual methods have been particularly effective in bringing out the views of children in a range of socioeconomic settings (129, 130). The right to education featured in the top three issues in three quarters of these groups (131). In a refugee programme in Jhapa, Nepal, children with disabilities were found to be a neglected and vulnerable group (132). A full-time disability coordinator for the programme was therefore appointed to undertake participatory action research. Disabled children talked about their family lives and described how they were taunted if they left their homes. After 18 months more than 700 children had been integrated into schools, and sign-language training had been introduced in all refugee camps, for Deaf and non-deaf children.

Evaluations of the technical accessibility provisions in high-income settings have found that wheelchair clearance and space requirements are often too low (49 antibiotics for urinary tract infection in cats order cefdinir 300mg, 50) antibiotic 8 month old buy discount cefdinir 300mg. These shortcomings stem from the changing characteristics of assistive technology such as bigger wheelchairs antibiotics for sinus infection in horses purchase cefdinir 300mg with mastercard, from the advances in knowledge about how to facilitate access antibiotic names starting with z buy cefdinir 300mg overnight delivery, and from the time lag for incorporating new knowledge into standards. The basic features of access in new construction should include: provision of curb cuts (ramps) safe crossings across the street accessible entries an accessible path of travel to all spaces access to public amenities, such as toilets. A compilation of data on 36 countries and areas in Asia and the Pacific showed that 72% have accessibility standards for either the built environment or public transport or both. An assessment of the content of standards and coverage is required to understand the scope and application of these norms (51). Most accessibility standards concentrate on the needs of people with mobility impairments. The relevant standards, for instance, contain many criteria to ensure enough space and manoeuvring clearances for wheelchair and walkingaid users. It is also important to meet the needs of people with sensory impairments, primarily avoiding hazards and finding the right way. To this end, communication methods have been devised including visual alarms and better contrasts on signs, Braille signage, tactile 174 paving, and dual modes on interactive devices, such as automated teller machines in banks and ticket machines. Accessibility standards rarely explicitly address the needs of people with cognitive impairments or mental health conditions. Universal design guidelines do deal with matters such as better support for finding the way and for reducing stress which can be considered in accessibility standards (52). A study on accessibility in rural villages in Gujarat, India, found that current practices in affluent urban areas in India were not appropriate in these villages (53). Other studies on accessibility for persons with disability in developing countries have focused on hygiene and the use of water (54, 55) and proposed simple, low-cost solutions to make toilet facilities, water-carrying devices, water stands, and other facilities accessible. Standards on accessibility are also needed in refugee camps and in informal settlements and reconstruction projects after a disaster. Studies of informal settlements in India and South Africa have found that the conditions there, as in poor rural areas, require different approaches to accessibility than urban areas providing access to squat toilets and overcoming open drains, which create obstacles for wheelchair and pedestrian use. The serious security and privacy barriers in these communities are as important as independence in carrying out daily tasks (56). The Sphere Handbook, developed by more than 400 organizations around the world, sets out the minimum standards in a disaster response and includes approaches for meeting the needs of people with disabilities. In its 2010 update disability is addressed as an issue cutting across all the main sectors, including water supply, sanitation, nutrition, food aid, shelter, and health services (57). Standards in industrialized countries have driven a "global convergence" in accessibility standards (8) rather than standards in developing countries reflecting cultural or economic conditions (58). Whether this accounts Chapter 6 Enabling Environments for the lack of implementation of accessibility laws and standards in many countries requires further research. The International Organization for Standardization developed an international accessibility standard using a consensual approach, though not all regions of the world are represented on the committee (59). International and regional organizations can help improve standards by providing recommendations for member countries. The European Concept for Accessibility Network has taken this approach by publishing a technical manual to help organizations develop standards and regulations incorporating universal design (60). An international effort is needed to develop standards appropriate for different stages of policy evolution, different levels of resources, and cultural differences in construction. Government funding agencies including those that fund health care facilities, transportation, and schools can also review plans as part of their approval process, using consistent standards. Accessibility audits can also be conducted by disability organizations or even by individual citizens. In Malaysia, for example, groups working on behalf of disabled people are completing audits of major hotels (see Box 6. The lead agency A lead government agency can be designated to take responsibility for coordinating the activities of other bodies involved with accessibility, particularly those that fund the construction of public buildings and monitoring the implementation of laws, regulations, and standards. Furthermore, it could oversee the licensing of design professionals, businesses, and services to ensure that accessibility is part of professional training curricula.
For example virus informaticos discount cefdinir uk, a child may begin to squirm and yell while riding because he needs to use the bathroom and has difficulty otherwise making his needs known antibiotics gas purchase 300mg cefdinir fast delivery. Coxarthrosis Coxarthrosis is the degeneration of the hip joint and is characterized by the destruction of the joint cartilage and abnormal bone growth infection gum order cefdinir toronto. It is accompanied by pain and stiffness antibiotics good or bad purchase 300mg cefdinir visa, particularly after prolonged activity, and by decreased range of motion. Contraindication: · Mounted seated activities place extreme stress on the hip joint. The hip motion required for mounting, riding astride and dismounting could cause further injury to the joint or hasten the course of the disease. Cranial Defects this condition is characterized by the absence of a portion of the skull. The risk of seizures increases for individuals with cranial deficits (see Seizure Disorders). Diabetes insipidus is a disorder resulting from a deficient production of the hormone vasopressin and leads to similar symptoms of excessive thirst and urination. Diabetes may be associated with other serious medical conditions, such as low resistance to infections, ulcerations of the extremities, cardiovascular and kidney disorders, disturbances in electrolyte balance, eye disorders and disturbance of sensation. People with diabetes require a balance of activity level and food intake to control their diabetes, whether they take medication or not. Refer to a first aid manual for signs and emergency treatment of insulin reaction and diabetic shock. The skin should be monitored for areas of redness that persist for 15 to 20 minutes after mounted activities. Also, during these activities monitor the lower extremities for swelling and discoloration and look for areas with an absence or decrease in sensation. Precaution: · If sensation is absent or impaired (See Skin Integrity) Contraindication: · Uncontrolled diabetes and/or medically unstable conditions associated with diabetes · Skin Integrity on the weight-bearing surfaces Eating Disorders · Anorexia Nervosa Anorexic conditions are those of extreme weight loss due to an eating disorder. Bulimic participants may exhibit mood swings, acting out, poor judgment regarding safety and secretive bingeing and purging behaviors. Monitoring of electrolyte levels and energy expenditure by the medical professionals should be done to determine the appropriateness of physical activity for that participant. For those participants with eating disorders such as anorexia or bulimia, caution should be taken that these participants regard the rules/guidelines of the operating center. Standards for Certification & Accreditation 2018 Contraindication: · If electrolyte levels are significantly out of balance · If adequate supervision of the participant is not available · Obesity Excessive weight problems may be a primary condition such as an eating disorder or congenital condition; or secondary to medical issues such as side effects of medication or thyroid dysfunction. In either case, safety of the participant, equine and staff are the major consideration. Precaution: · Poor endurance caused by breathing difficulties or circulatory problems (see Respiratory Compromise, Fatigue/Poor Endurance, Heart/Cardiac) · Skin chafing or pinching (see Skin Integrity) Contraindication: · If the staff is unable to safely manage the participant in any situation, including an emergency dismount, and is at risk for harming themselves or the participant · If safety or comfort of the equine is compromised during mounted activities potentially resulting in a fight or flight response, which in turn could harm the staff or participant · Pica A disorder that causes strong cravings for non-food items. The diagnosis is given only once this becomes a persistent behavior, lasting more than four weeks. Obvious difficulties are the ingestion of parasites, toxic substances or gastrointestinal upset. Incomplete sexual development and a chronic feeling of hunger that, coupled with a metabolism that uses drastically fewer calories than normal, can lead to excessive eating and life-threatening obesity. Equipment/Medical Devices There are many pieces of equipment that a participant might need for improved function. Some examples of equipment seen at Professional Association of Therapeutic Horsemanship International centers may include: External: eyeglasses, hearing aids, braces/orthotics for the trunk or for the extremities (see Spinal Orthosis), supplemental oxygen, suction (oral, tracheal), augmentative communication devices, etc. Standards for Certification & Accreditation 2018 203 Internal: cochlear implants, feeding tubes, tracheostomies, internal pumps (baclofen, morphine, insulin or other medication administration), shunts, pacemakers, mouthguards/retainers, indwelling catheter (suprapubic or urethral), ostomy or colostomy bags, etc. Staff training and animal desensitization must be conducted with all specialized medical equipment. They may be essential, or they may not be needed prior to , during or after the activity. Consult with the participant, family or medical professionals to determine the benefits and risks of using some of the equipment during equine activities. Alternative methods of mounting/ dismounting and/or possible tack adaptations may be required to avoid disturbing the external port.
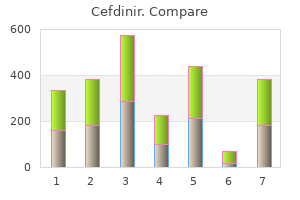
There is a concern as to the definition of what an "outlier prescriber" is and to avoid arbitrary limitations without taking into account the provider expertise and the patient demographic 7daystodie infection discount cefdinir express. Careful consideration of how outliers will be defined is needed to avoid patient harm infection medicine buy cheap cefdinir 300mg online. Patient care should be based primarily on the clinical context and the patient-clinician interaction bacteria on hands discount cefdinir 300 mg on-line. Opioid stewardship programs can provide a holistic am 7200 antimicrobial buy discount cefdinir line, efficient, comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to address safer opioid prescribing within a health system, thus empowering cross-disciplinary collaboration and inclusion with the development of measures to guide implementation and successful efforts. It is essential to ensure that careful consideration of clinical context is always considered. Appropriate treatment can be delayed or denied because of unavailability and, in other cases, result in the use of second-line, less effective alternatives. Patient safety events - namely, medication errors - are more likely to occur during times of shortages because of the increased prescribing of less familiar pharmacologic agents. For instance, a retrospective chart review of patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit during a 20112012 peak shortage of injectable benzodiazepines. Morphine, hydromorphone, and fentanyl are the most commonly used opioid injectables because of their fast and reliable analgesic effects and because they offer a viable option for patients unable to tolerate oral administration. Moreover, there is substantial variability in the availability and structure of guidance regarding the data needed to qualify for coverage provided to developers working on innovative nonpharmacologic treatments. In the absence of a national coverage policy, an item or service may be covered at the discretion of the Medicare contractors based on a local coverage determination. Such practice leads to variation in coverage of items and services that can affect medical care. The inconsistencies in insurance policies, the variability in guidance regarding coverage determinations, and the variability in utilization management tools that coverage providers use can cause delays in service delivery, provision of inadequate treatment, and added financial and psychosocial burden for patients with pain. Consistently forcing providers to try a series of non-first-line treatments prior to authorizing treatment plans can be problematic, hindering appropriate patient care, creating tremendous inefficiency, and resulting in a loss of time and resources. In addition, reimburse care team leaders for time spent coordinating patient care. Pain management specialists possess expertise and are specially trained in the evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment of acute and chronic pain. Likewise, access to behavioral pain management is limited because financial incentives are lacking for psychologists and other providers to specialize in pain. Many insurance programs do not reimburse for behavioral pain treatments, or they reimburse at a much lower rate than for pharmacologic or interventional treatments. Because of the lack of incentives, not enough providers are trained in behavioral pain management. Furthermore, there is a shortage of multidisciplinary pain management teams to care for patients with complex pain conditions and physical and psychological comorbidities. Enhancements should be made in professional school curricula, postgraduate training programs, and continuing education courses. Resources include governance and guidance as well as research and funding opportunities. New knowledge development is needed in various areas of pain research, with emphasis placed on molecular and cellular mechanisms of pain, the genetics of pain, bio-behavioral pain, and preclinical models of pain. As novel and proven treatment options emerge to improve acute pain and specific chronic pain conditions, they should be rapidly incorporated. Allocate funding to develop innovative therapies and build research capabilities for better clinical outcomes tracking and evidence gathering. Furthermore, given the current state of the overdose crisis, further drastic reduction of clinician prescribing alone may not have a large effect on decreasing opioid overdose deaths in the short term. Various organizations, such as the American College of Physicians, supported the guideline when it was initially released, but clinicians, patients, professional organizations, and other stakeholders have highlighted important limitations since its publication. The Task Force respectfully points out that there is little clinical trial evidence showing that opioids lack clinical efficacy for such patients. Long-term studies of therapies for chronic, moderate, or severe pain are difficult to conduct because of patient drop-out for ineffective treatment.
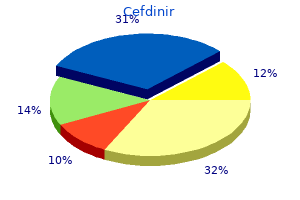
Clinical outcome in adult onset idiopathic or paraneoplastic opsoclonusmyoclonus bacteria zapper for face buy discount cefdinir 300mg line. Cross References Ocular flutter; Saccadic intrusion antibiotic 3 pack purchase cefdinir 300 mg otc, Saccadic pursuit; Square wave jerks Optic Aphasia Optic aphasia is a visual modality-specific naming disorder 0157 infection buy cefdinir 300mg cheap. It has sometimes been grouped with associative visual agnosia virus total purchase 300 mg cefdinir, but these patients are not agnosic since they can demonstrate recognition of visually presented stimuli by means other than naming. Moreover, these patients are not handicapped by their deficit in everyday life, whereas agnosic patients are often functionally blind. Objects that are semantically related can be appropriately sorted, indicating intact semantics. This is not simply anomia, since the deficit is specific to visual stimuli; objects presented in tactile modality, or by sound, or by spoken definition, can be named. Perception is intact, evidenced by the ability to draw accurately objects which cannot be named. Optic aphasia is associated with unilateral lesions of the left occipital cortex and subjacent white matter. A visual-speech disconnexion syndrome: report of a case with optic aphasia, agnosic alexia and colour agnosia. Tactile search with the palm and fingers may be undertaken in searching for an object, using somatosensory cues to compensate for impaired access to visual information. Hence this may be characterized as a modality-specific apraxia, wherein visual information cannot be used to guide goal-directed movements. Optic ataxia occurs with lesions of the intraparietal sulcus and regions medial and superior to it; the primary visual cortex is intact. The temporal disc may appear pale in a normal fundus, so that optic atrophy can only be confidently diagnosed when there is also nasal pallor, although temporal pallor may follow damage to the macular fibre bundle with central visual defects. Optic atrophy may be the consequence of any optic neuropathy which causes optic nerve damage leading to gliotic change of the optic nerve head. Although most often seen with optic nerve pathology, it may be a consequence of pathology in the retina, optic chiasm, or optic tract. In clinical practice a striped drum serves to test both visual pursuit and saccades. Rotation of the stripe to the left produces leftward pursuit, followed by a compensatory saccade to the right, followed by pursuit to the left of the next stripe, with another compensatory saccade, and so on. Clinical and imaging studies show a strong correlation between oro-facial dyspraxia and lesions in the frontal operculum; it may also occur with subcortical lesions involving periventricular and/or peristriatal white matter as well as the basal ganglia. Progressive loss of speech output and orofacial dyspraxia associated with frontal lobe hypometabolism. Normally there is a drop in blood pressure of lesser magnitude on standing but this is usually quickly compensated for by the baroreceptor reflex. Measuring blood pressure automatically by passive head-up tilt testing (tilt table) is also helpful in diagnosing orthostatic hypotension if the active standing test is negative, and the history is suggestive, or in patients with motor impairment. There may be supine hypertension and reversal of the normal circadian blood pressure rhythm (normally lower at night), with an increased frequency of micturition at night. Other features of autonomic dysfunction may be present, including dry eyes and dry mouth (xerophthalmia, xerostomia), a tendency to constipation, and lack of penile erections. GuillainBarrй syndrome, amyloidosis) However, the most common cause of orthostatic hypotension in hospital practice is probably dehydration or overzealous treatment with antihypertensive or diuretic agents. Management of orthostatic hypotension consists of education on factors that influence blood pressure. Non-pharmacological approaches include increased salt and water intake, head-up bed tilt, and wearing elastic stockings or a G-suit. Pharmacological therapies include fludrocortisone (first line), and midodrine, ephedrine, or dihydroxyphenylserine (second line). Oscillopsia is most often due to acquired bilateral loss of vestibular function (loss of the vestibulo-ocular reflexes). Oscillopsia does not occur in congenital nystagmus, nor in opsoclonus, presumably due to the operation of the visual suppression mechanism which normally operates during saccadic eye movements. Oscillopsia: impaired vision during motion in the absence of the vestibulo-ocular reflex.
Effective cefdinir 300 mg. Course trailer: Bacterial Genomes: Disease Outbreaks and Antimicrobial Resistance.


